GPS or Global Positioning System is a satellite based Global Navigation System owned by the U.S. that provides exact location, navigation and timing services to civilian users on a continuous world wide basis. Anyone with a GPS receiver and unobstructed line of sight to 4 or more GPS satellites can access these services, anywhere and at any time or weather.
 .jpg)      
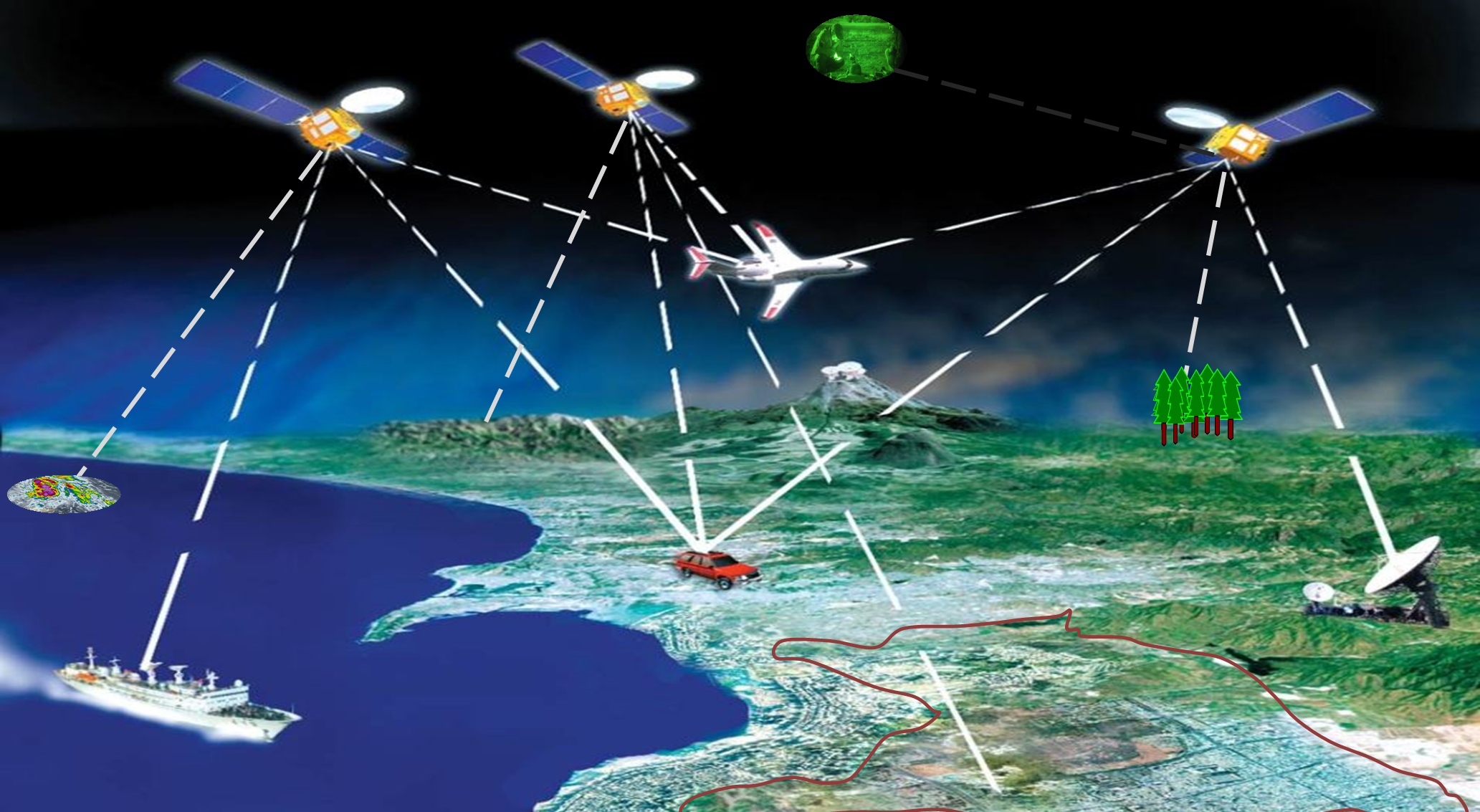
GPS consists of three (segments):
1. The Space Segment - A network of 24 GPS satellites orbiting the earth transmitting one way signals that give the current GPS satellite position and time.
2. The Control Segment - Control and monitoring stations on the earth that maintain the satellites in their proper orbits through occasional command maneuvers, and adjust the satellite clocks. It tracks the GPS satellites, uploads updated navigational data, and maintains health and status of the satellite constellation, and
3. The User Segment - The GPS receiver equipment owned by users, which receives the signals from the GPS satellites and uses the transmitted information to calculate the user's three-dimensional position and time.
The Space and Control segment are developed, maintained and operated by the U.S. Air Force.
Basic Concept of GPS
  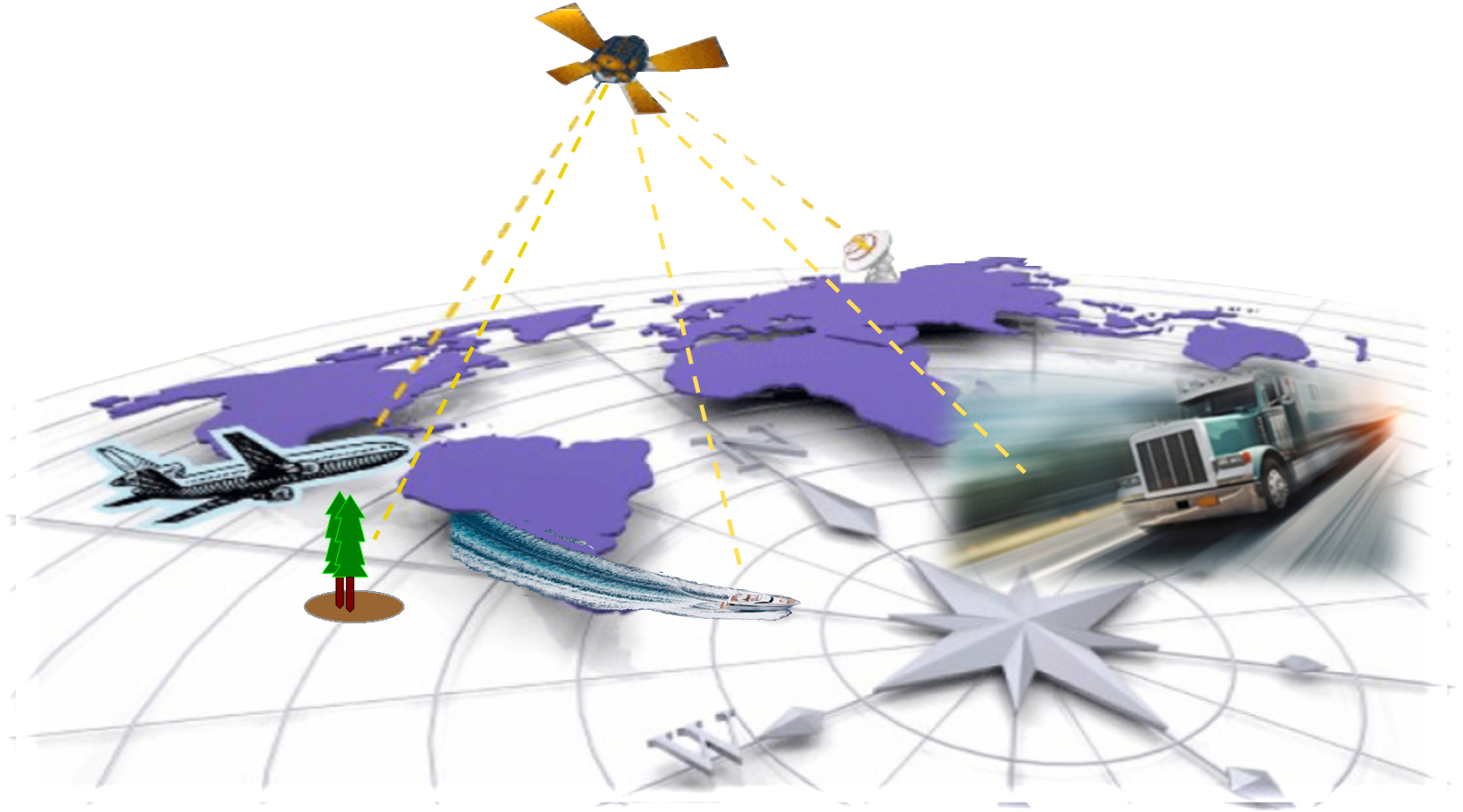
A GPS receiver calculates its position by precisely timing the signals sent by GPS satellites high above the Earth. Each satellite continually transmits messages that include
1. the time the message was transmitted
2. precise orbital information (the ephemeris)
3. the general system health and rough orbits of all GPS satellites (the almanac).
The receiver uses the messages it receives to determine the transit time of each message and computes the distance to each satellite. These distances along with the satellites' locations are used with the possible aid of trilateration, depending on which algorithm is used, to compute the position of the receiver. This position is then displayed, perhaps with a moving map display or latitude and longitude; elevation information may be included. Many GPS units show derived information such as direction and speed, calculated from position changes.
Sources:
1. Wikipedia
2. Official US Government Website
|